Hiatal Hernia Treatment in Agra | Laparoscopic Surgery by Dr. Shwetank Prakash
Call Us when you Need Help!
Hiatal Hernia: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
A hiatal hernia occurs when a portion of the stomach pushes through the diaphragm into the chest cavity. This condition can lead to acid reflux, heartburn, and difficulty swallowing. While mild cases can be managed with lifestyle changes and medications, severe hiatal hernias may require laparoscopic surgery for permanent relief.
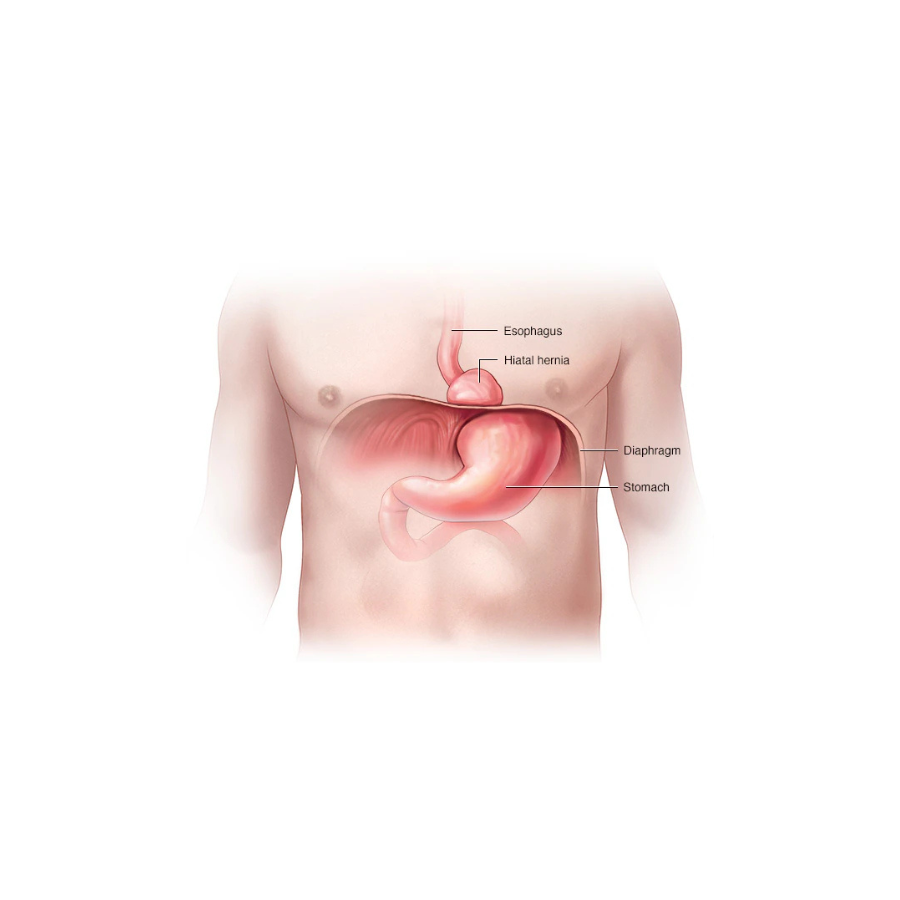
Understanding Hiatal Hernia
The diaphragm is a muscle that separates the chest from the abdomen. It has a small opening, called the hiatus, through which the esophagus passes before connecting to the stomach. A hiatal hernia occurs when part of the stomach bulges through this opening into the chest.
Types of Hiatal Hernias
1. Sliding Hiatal Hernia (Most Common Type)
- The stomach and lower esophagus slide up into the chest temporarily.
- Symptoms occur mostly when lying down or after eating.
- Often associated with GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease).
2. Paraesophageal Hiatal Hernia (Less Common but Serious)
- Part of the stomach pushes through the diaphragm but does not return to its normal position.
- Can lead to serious complications like strangulation (cutting off blood supply).
- Often requires surgical intervention.
What Causes a Hiatal Hernia?
Hiatal hernias develop due to increased pressure on the abdomen and weakening of the diaphragm muscles.
Common Causes Include:
- Chronic coughing or straining during bowel movements
- Obesity (increased pressure on the abdomen)
- Aging (diaphragm muscles weaken over time)
- Heavy lifting or physical exertion
- Pregnancy (hormonal changes and abdominal pressure)
- Previous abdominal surgery or trauma
Who Is at Risk?
Certain individuals have a higher risk of developing a hiatal hernia, including:
- People over 50 years old (muscle weakness increases with age)
- Obese individuals (excess weight increases pressure on the stomach)
- Chronic smokers (coughing weakens the diaphragm)
- Patients with acid reflux (GERD) (weakened esophageal muscles)
- Individuals with a family history of hiatal hernias
Symptoms of a Hiatal Hernia
Mild hiatal hernias may not cause noticeable symptoms. However, larger hernias can lead to:
- Frequent heartburn and acid reflux
- Chest pain or burning sensation
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
- Chronic cough or sore throat
- Regurgitation of food or sour liquid
- Shortness of breath (in severe cases)
If a paraesophageal hernia becomes strangulated, it can lead to:
- Severe chest or abdominal pain
- Vomiting or inability to eat
- Internal bleeding (black stools or vomiting blood)
A strangulated hiatal hernia is a medical emergency and requires immediate surgery.
Complications of an Untreated Hiatal Hernia
If left untreated, a hiatal hernia can lead to:
- Chronic GERD (acid reflux disease), increasing the risk of esophageal damage
- Esophagitis (inflammation of the esophagus)
- Esophageal ulcers and bleeding
- Barrett’s Esophagus, a precancerous condition due to long-term acid exposure
- Aspiration pneumonia, caused by stomach contents entering the lungs
- Strangulated hernia, cutting off blood supply to the stomach
Diagnosis of Hiatal Hernia
A hiatal hernia is diagnosed through:
- Upper Endoscopy (EGD): A thin tube with a camera examines the esophagus and stomach.
- Barium Swallow X-ray: The patient drinks a contrast liquid to highlight the hernia on X-rays.
- Esophageal Manometry: Measures pressure and function of the esophagus and lower sphincter.
Treatment Options for Hiatal Hernia
1. Lifestyle Modifications (For Mild Cases)
- Eat small, frequent meals instead of large portions.
- Avoid spicy, acidic, and fatty foods that trigger reflux.
- Maintain a healthy weight to reduce abdominal pressure.
- Elevate the head of your bed while sleeping to prevent reflux.
- Quit smoking and alcohol consumption.
- Avoid lying down immediately after eating.
2. Medications for Symptom Management
- Antacids (neutralize stomach acid)
- Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs) (reduce acid production)
- H2 Blockers (lower stomach acid levels)
- Prokinetics (improve esophageal motility)
These medications help control acid reflux symptoms, but do not treat the hernia itself.
3. Laparoscopic Hiatal Hernia Surgery (For Severe Cases)
When symptoms persist despite medication or if the hernia is large, surgery is the best option.
Laparoscopic Nissen Fundoplication is the gold standard for hiatal hernia repair.
- Minimally invasive (small incisions, faster recovery)
- The upper stomach is wrapped around the esophagus to prevent acid reflux.
- The hiatus opening is reinforced to prevent future hernias.
4. Open Surgery (For Large or Strangulated Hernias)
In rare cases, an open surgical approach may be necessary, especially if:
- The hernia is too large to be repaired laparoscopically.
- The stomach is strangulated, cutting off blood supply.
Hiatal Hernia Surgery Recovery and Aftercare
- Most patients can go home the next day after laparoscopic surgery.
- Mild discomfort is common but managed with medications.
- Soft diet is recommended for a few weeks to allow healing.
- Avoid heavy lifting and strenuous activity for at least 4–6 weeks.
- Reflux symptoms improve significantly after surgery, leading to better quality of life.
Get expert hiatal hernia treatment in Agra with
Dr. Shwetank Prakash, a specialist in minimally invasive laparoscopic surgery.
Fast relief from acid reflux, heartburn, and chest pain.
Book a consultation today!
Why Choose Dr. Shwetank Prakash for Laparoscopic Minimal Invasive Surgery in Agra?
Choosing Dr. Shwetank Prakash for Minimally Invasive laparoscopic surgery in Agra ensures expert surgical care, the latest minimally invasive techniques, and a patient-first approach. Dr. Prakash is a highly experienced laparoscopic and minimally invasive surgeon, with a focus on precision, safety, and faster recovery.
- Faster recovery as minimally invasive techniques reduce downtime
- Minimal scarring due to small incisions leading to better cosmetic outcomes
- Less postoperative pain compared to traditional open surgery
- Lower risk of complications with advanced techniques ensuring safety and precision
Patient-Centric Approach
Dr. Prakash is known for his personalized treatment plans, ensuring every patient receives individualized care. His detailed consultations include:
- A clear understanding of the procedure
- Explanation of potential risks and expected outcomes
- Complete transparency to help patients feel confident about their treatment
- With a proven track record of successful surgeries and high patient satisfaction
- Dr. Shwetank Prakash is a leading expert in gallbladder and Kidney stone removal surgery in Agra.
FAQs
There are many questions about the service, we have selected frequently asked questions about this service. If you do not see your answer, please contact us.
What is minimally invasive laparoscopic surgery?
What are the advantages of laparoscopic surgery over traditional open surgery?
Smaller incisions and minimal scarring
Reduced pain and discomfort
Shorter hospital stay and faster recovery
Lower risk of infections and complications
Quicker return to daily activities
What types of conditions can be treated with laparoscopic surgery?
Gallbladder removal (cholecystectomy)
Hernia repair
Appendix removal (appendectomy)
Kidney stone and prostate surgery
Weight loss (bariatric) surgery
Gastrointestinal and colorectal surgeries
Is laparoscopic surgery safe?
How long does it take to recover from laparoscopic surgery?
Will I have visible scars after laparoscopic surgery?
Is laparoscopic surgery painful?
Do I need to stay overnight in the hospital after laparoscopic surgery?
What precautions should I take after laparoscopic surgery?
Follow the prescribed diet and medications
Keep the incision area clean and dry
Attend follow-up appointments for recovery assessment
Who is a good candidate for laparoscopic surgery?
Why Choose Us?
Are you having health problems? Contact us today!
Address Business
Contact With Us
Call Us 24/7: 81 22 22 22 22
